Research Projects
-
SELFLED - Selective fluorescence microscopy of single cells based on highly integrated microLED arraysThe joint research project SELFLED is working on a new type of miniaturized illumination unit for fluorescence microscopy. Optical simulations and algorithms will be used to design microlens arrays that influence the beam level of microLEDs in such a way that individual cell samples can be selectively illuminated and examined.Led by: M. Sc. Anna-Lena FritzeYear: 2024Funding: BMBFDuration: 01.01.2024 - 31.12.2026
![]()
![]()
-
FlexBiPOF - Flexo-printed Coupling System for Bidirectional Operation of Polymer Optical FibresThe aim of this research project is to develop an optical transceiver that makes it possible to operate a polymer optical fibre (POF) in two communication directions. This requires a waveguide element that is produced additively by flexography.Led by: M. Sc. Janka KirsteinYear: 2024Funding: ZIMDuration: 01.05.2024 - 30.04.2026
![]()
![]()
-
Multifunctional Measurement System for Microgravity ResearchThe aim of this research project is to develop a sensor system for research in weightlessness. The system should be able to record and process relevant data.Led by: M. Sc. Richard SperlingYear: 2024Funding: Ministry of Science and Culture of Lower Saxony (MWK)Duration: 01.01.2024 - 30.06.2024
![]()
![]()
-
AME 2.0 - New development of a 3D printer for quality-optimized additive manufacturing of rubber-based moulded partsThe Additive Manufacturing of Elastomers- (AME)-process from the previous Elastomer-3D project is being optimized as part of this project. A new 3D printer is being developed for this purpose, which will be used especially for additive manufacturing of industrial components.Led by: M. Sc. Sebastian LeineweberYear: 2024Funding: German Aerospace Center (DLR)Duration: 01.04.2024 - 31.03.2026
![]()
![]()
-
Development of a multi-user facility for quantum experiments in the Einstein-Elevator by integrating an ISS express rackThe project aims to develop a multi-user express rack that serves as an interface between the Einstein-Elevator and the scientific experiments on the ISS and is based on the standardized sizes of the International Standard Payload Rack (ISPR). Technical specifications such as power supply, communication systems, and cooling must be adapted to the special environmental conditions of the Einstein-Elevator to support and validate current and future ISS research projects efficiently.Led by: M. Sc. Marvin RaupertYear: 2024Funding: QuantumFrontiersDuration: 01.07.2024 - 31.12.2024
![]()
![]()
-
Microgravity Assembly for Acceleration TestingThe aim of this research project is to develop a module that records and evaluates microgravity data within an Orbital Paradigm orbiter. The orbiter is to be used within low Earth orbit.Led by: M. Sc. Richard SperlingYear: 2024Duration: 01.06.2024 - 31.12.2026
![]()
![]()
-
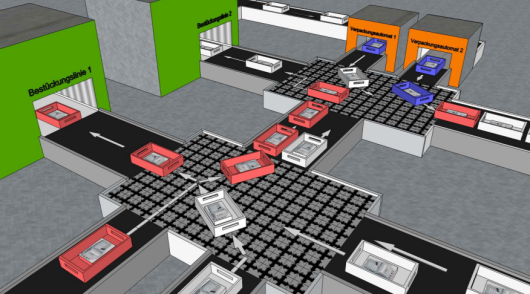
ModHalbo - Development and validation of a novel transportation and storage concept using interconnected multidirectional heavy-duty conveyor modulesThe aim of this research project is to develop a new type of modular warehouse floor for omnidirectional transportation in intralogistics. The floor should be able to carry a load of 9 tons so that the operational process does not have to be interrupted.Led by: M. Sc. Pavel Bakhteev, M. Sc. Felix WentzienYear: 2024Funding: Forschungsgemeinschaft Intralogistik/Fördertechnik und Logistiksystem e.V (IFL)Duration: 01.08.2024 - 31.01.2027
![]()
![]()
-
Ultrasonic levitation as a handling tool for ISM processesThe joint project Lev4ISM pursues the development of an innovative, resource-saving manufacturing process for In-Space Manufacturing (ISM), which aims to enable the substrate-free production of components in microgravity. By using acoustic levitation and implementing coupled simulations, the precise handling of particles and components in microgravity will be researched to create long-term solutions for sustainable and flexible space missions.Led by: M. Sc. Jan RaffelYear: 2023Funding: German Aerospace Center (DLR)Duration: 01.09.2023 - 31.08.2025
![]()
![]()
-
LernFFZ - Imitation learning for the transfer of human skills to industrial trucksThe aim of the research project is to extract and transfer human driving skills to semi-automated industrial trucks. The approach is based on imitation learning methods. This new control approach is intended to enable the industrial truck to autonomously pick up load carriers located in any position in the room.Led by: M. Sc. Mirko Schaper, M. Sc. Justus LübbehusenYear: 2023Funding: BMWKDuration: 01.12.2023 - 30.11.2026
![]()
![]()
-
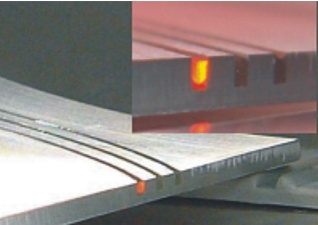
3D-MosquitOprint3D-MosquitOprint researches the integration of optically transparent waveguides in cavities on three-dimensional circuit carriers. The manufacturing process is based on the Mosquito method, in which a light-conducting core is dispensed into a liquid cladding polymer. Afterwards, the structure is cured by UV light. For use as electro-optical hybrid components, there are also investigations into efficient coupling between manufactured waveguides and diodes. For this purpose, the end surfaces are prepared and assembled with diodes.Led by: M. Sc. Laura FüttererYear: 2022Funding: AiF (IGF)Duration: 01.07.2022 - 30.06.2024
![]()
![]()
-
Levitated Magnets for Quantum MetrologyThis project aims at a systematic investigation of sensors based on levitated micromagnets, which allow to measure ultra-low torques and magnetic fields, demonstrating an unprecedented energy resolution.Led by: M. Sc. Alexander HeidtYear: 2022Funding: QuantERA Project of the EU (DFG)Duration: 01.01.2022 - 31.12.2024
![]()
![]()
-
Activity of comets under partial gravityCometary activity, which in this case refers to the ejection of dust from the surface, can be simulated in the laboratory, but more than a thousand times Earth's gravity overrides the gravity prevailing on comets. With the help of the Einstein-Elevator it will be possible to perform experiments under comet-like conditions.Led by: M. Sc. Emre TahtaliYear: 2022Funding: German Aerospace Center (DLR)Duration: 01.08.2022 - 31.07.2025
![]()
![]()
-
Future Conveyor Drive - Monetary and ecological belt conveyor optimisation by means of driven idlersWithin the framework of this research project, the monetary and ecological optimisation of belt conveyor systems by means of driven idlers is being investigated. With help of a specially developed co-simulation environment, their influence on the operating behaviour and dynamic system stability of belt conveyor systems is analysed. The aim is to develop a selection logic for determining the optimised use of driven idlers for industry.Led by: M. Sc. Carsten SchmidtYear: 2022Funding: AIFDuration: 01.08.2022 - 31.07.2024
![]()
![]()
-
Hannover Center for Microgravity ResearchThe focus of the DFG-funded research center "Hannover Center for Microgravity Research" is the establishment of an administrative service and management structure for the Einstein-Elevator. This should enable effective use of the Einstein-Elevator, also for external scientists.Led by: Dr.-Ing. Christoph LotzYear: 2022Funding: DFGDuration: 01.01.2022 - 31.12.2024
-
DIGITRUBBER - Data mining and AI for optimized cross-process controlAs part of the collaborative project "Digital Rubber Processing - Using Extrusion as an Example" (DIGITRUBBER), an online characterization of the processed rubber compound is being developed by combining new measurement technology approaches, classical modeling and machine learning. This is intended to ensure production at optimum quality while reducing waste.Led by: M. Sc. Sebastian LeineweberYear: 2021Funding: BMBFDuration: 04/2021 – 03/2024
![]()
![]()
-
3D-multi layer prints of Mechatronic Integrated DevicesIn the 3D-MLD project, additive manufacturing for the generative production of multilayer circuits on spatial components is investigated. The novel approach is based on an alternating coating of the component surface with functional inks and local laser processing. Besides the laser sintering of conductor paths, laser ablation of the insulating coating enables the generation of vertical interconnect accesses in between the layers.Led by: Ejvind OlsenYear: 2021Funding: BMWiDuration: 04/2021 – 03/2023
![]()
![]()
-
Laser-based additive manufacturing of metal parts from powder in microgravityThe aim of this research project is the development of a laser-based additive manufacturing process for the production of metal parts from powder in microgravity. The approach is based on the "Laser Metal Deposition" (LMD) process known for earth gravity.Led by: M. Sc. Marvin RaupertYear: 2021Funding: DFGDuration: 07.2021 - 06.2024
![]()
![]()
-
Dark Energy Search with Atom Interferometry in the Einstein-ElevatorThe collaboration DESIRE uses the free-fall simulator Einstein-Elevator for dark energy search with atom interferometry. For this purpose the apparatus MAIUS-A will be reconstructed with a specialized test mass and afterwards operated in microgravity.Led by: M. Sc. Alexander HeidtYear: 2021Funding: German Aerospace Center (DLR)Duration: 01.04.2021 - 31.03.2024
-
Interferometry with entangled atoms in spaceIn this project, the entanglement of atoms in microgravity is measured using a robust and compact atomic sensor. The main goal is to demonstrate interferometric sensitivity beyond the standard quantum limit in microgravity.Led by: M. Sc. Alexander HeidtYear: 2021Funding: German Aerospace Center (DLR)Duration: 01.09.2021 - 31.12.2024
-
Experiment carrier for the Einstein-ElevatorAn essential Component of the Einstein Elevator at the Hannover Institute of Technology (HITec) is an experiment carrier, that is used inside the Einstein Elevators gondola. In collaboration with the German Aerospace Center (DLR), the Institute for Transport and Automation Technology is developing a low-vibration carrier. The aim is to use the system to carry out various experiments under microgravity.Led by: M. Sc. Richard SperlingYear: 2020Funding: DLR-SIDuration: 08.2020-07.2023
![]()
![]()
-
PhoenixD - Flexographic printing of optical networksThe PhoenixD research vision is to implement precision optical systems resource and cost-effectively by using additive manufacturing technology. For this purpose, researchers from mechanical engineering, physics, electrical engineering, computer science and chemistry intend to work together on the simulation, production and application of optical systems. So far, such systems usually consist of glass-based components tediously assembled in small batches, often even by hand. Experts from the various disciplines will aim to work together on a digitized production system that can realize individualized products. In this subproject, the production of planar optical network structures is being researched. For this purpose, a classic printing processes, the flexo printing, is used to enable a cost-effective production.Led by: M. Sc. Jonathan PleußYear: 2019Duration: 01.01.2019 - 31.12.2025
![]()
![]()
-
OptiK-NetThe BMBF project OptiK-Net comprises the possibility of integrating flexible optical conductor structures into the manufacturing process of conventional printed circuit boards in an application- and industry-oriented manner. Optical waveguides in electronic structures are considered difficult to implement in industry, but offer advantages and design possibilities over printed circuit boards with electrical conductor paths. In particular, their high bandwidth and low sensitivity to interference allow new solutions in communication networks. In the OptiK-Net project, obstacles are addressed to enable innovative industrial applications by implementing an exemplary process chain for the manufacture of an optoelectronic rigid-flex printed circuit boards. Within this process chain, two new approaches will be pursued: direct printing of optical waveguides and their direct integration into electrical circuit boards. For the direct printing of optical waveguides, flexographic printing, gravure printing and screen printing are considered as conventional printing processes. These processes enable a high output of similar waveguide structures, so that they can be evaluated with regard to their quality and capability as an industrial process. By integrating them into a rigid-flex composite, the communication of decoupled electrical circuits can be realized.Led by: M. Sc. Andreas EvertzYear: 2019Funding: BMBFDuration: 10/19 - 09/22
![]()
![]() © ITA
© ITA
-
PhoenixD - Electrical integration of optical networksImplementing optical precision systems quickly and cost-effectively using additive manufacturing: This is the vision of PhoenixD. In this subproject, research is conducted on the production of planar optical network structures. The optical coupling of the light sources to the optical waveguide, which is printed or dispensed, for example, is one of the research questions to be solved. Here, precise mounting and alignment to the end face of the waveguide is of enormous importance.Led by: M. Sc. Laura FüttererYear: 2019Duration: 01.01.2019 - 31.12.2025
![]()
![]()
-
Cold Plasma in ZeroGThe height dependence of the plasma conditions and the height dependence of the dynamics of charged microparticles inserted into the plasma are to be investigated in the Einstein-Elevator in a plasma chamber. To this end, the movements of the microparticles during the transition from 1 g to 0 g in the Einstein-Elevator are to be analyzed.Led by: Dr.-Ing. Christoph LotzYear: 2019Funding: German Aerospace Center (DLR)
![]()
![]()
-
3D-CopperPrint3D-CopperPrint investigates the use of additive manufacturing (3D printing) for the generation of copper interconnects on adaptive spatial circuit carriers. This process can be used to fabricate hybrid electro-mechanical components as an alternative to existing methods. The approach is based on the application of copper-filled coatings on the surface of three-dimensional objects and the subsequent photothermal laser sintering of the paths.Team:Year: 2018Funding: BMWi, AiF (IGF)Duration: 10/2018 – 06/2020
![]()
![]()
-
LinTrans-TransferDevelopment of a demonstrator for a directly propelled transport system using a linear motor.Year: 2017Funding: DFGDuration: 04/2017 – 12/2018
![]()
![]()
-
Tailored Light – Intelligent photoelectric surface made of light emitting modulesThe progress over the last decades in miniaturizing chips, wireless data transfer technologies and low-power consumption electronic devices has made it possible to design component-integrated autonomous sensors. These networks have a big potential for widespread use in maintenance prediction of manufacturing equipment, in intelligent building management systems and energy saving smart grids.Year: 2017Funding: Lower SaxonyDuration: 01/2017 – 01/2020
![]()
![]()
-
Automatable method for splice preparation of steel cord conveyor belts by means of beam technologyThe automation of splice preparation of steel cord conveyor belts is currently being researched at the Institute of Transport and Automation Technology (ITA) in collaboration with the Subaqueous Technical School of the Institute of Materials Science (IW). This is to enable the consistent quality of the connection as well as an increase in strength. This reduces operators’ risk of possible downtimes and the associated costs. An increase in strength also enables increased mass flows and therefore increases the productivity of the system.Year: 2017Funding: AiF, IFLDuration: 01/2017 – 12/2018
![]()
![]()
-
Mittelstand 4.0 competence center HannoverThe “Mit uns digital! Das Zentrum für Niedersachsen und Bremen” is the first of eleven centers that are currently being developed throughout Germany to support medium-sized enterprises and craftsmen’s businesses in their digital transformation with well-prepared information, examples and qualification.Year: 2017Funding: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and EnergyDuration: 12/15–11/18
![]()
![]()
-
Grid-supported fiberglass melting coupler for selective transversal mode couplingThe principle and the manufacture of a novel transversal mode-selective fiber fusion coupler is to be explored in this research project funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG). With selective mode coupling, different modes can be used as individual transmission channels, thus increasing the transmission bandwidth proportionally to the number of used modes. An essential feature of the new coupler is the selective transversal mode coupling by means of optical lattice.Year: 2016Funding: DFGDuration: 03/2016 – 02/2018
![]()
![]()
-
LaPOF – Laser active polymer optic fibersThe LaPOF project aims to research technological foundations for innovative laser-active polymer optical fibers as well as their production.Year: 2016Funding: European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)Duration: 12/2016–11/2019
![]()
![]()
-
New drive concept for belt conveyor systems on the basis of directly driven load-bearing rollersThe aim of this research project is the abolition of the current economic and technical length restrictions for belt conveyor systems in the area of mining and surface mining through the use of propelled load-bearing rollers.Year: 2016Funding: AIF, IFLDuration: 05/2016 – 04/2018
![]()
![]()
-
HYMNOS – Hybrid Numerical Optical SimulationNumerical methods for the calculation of light distributions in optical media can profit significantly from current trends in computer technology. The aim of this project is therefore the combination of different modeling approaches on different temporal and spatial scales. For this purpose, different aspects from interdisciplinary subject areas in physics and engineering sciences are investigated using models.Year: 2015Funding: Lower SaxonyDuration: 10/2015 – 09/2018
![]()
![]()
-
SFB 1153 – A4 Local adaptation of material properties on forming blanks by weld cladding to produce graded hybrid componentsThe sub-project is aimed at the manufacture of novel hybrid components from material combinations. This is where local, load-dependent property profiles are imprinted on the components. In order to achieve this, materials are applied to forming blanks by means of build-up welding. The material quantity and position are crucial for the targeted placement of the materials through forming.Year: 2015Funding: DFGDuration: 07/2015 – 06/2019
![]()
![]()
-
OPTAVER – Research group optical assembly and connection technology for optical bus systemsThe research focus of the sub-project TP1 of the research group OPTAVER is the conditioning of flexible substrates for the application of optical waveguides.Year: 2015Funding: DFGDuration: 2015-2021
![]()
![]()
-
Networked, cognitive production systems (netkoPs)Intelligent networking in production – a contribution to the future project Industry 4.0Year: 2013Funding: BMBFDuration: 11/2013 - 01/2017
![]()
![]()
-
VIPlets – Evidence of the aerodynamic potential of riblets produced by grinding and laser removal in a highly loaded axial compressorIn order to increase the power density and the efficiency in gas turbines and in particular in aircraft engines, minimizing aerodynamic losses remains one of the main targets. An innovative approach to this is the microstructuring of the overflow surfaces of the blading with riblets known from bionics. These small longitudinal riblets can reduce flow losses in the viscous sublayer of the turbulent boundary layer.Year: 2013Funding: BMBF – VIPDuration: 05/2013-04/2017
![]()
![]()
-
TRR 123 PlanOS – A05 Optodic bonding of electro-optically integrated circuits on film substratesIf one imagines a film as a sensor network with fully integrated optical functionalities for collecting various physical values, e.g. temperature, pressure and humidity, then light sources and detectors have to be integrated in the film and also have to be connected to the outside world. In this project, the issue of how the light sources and detectors can be incorporated into the film or be contacted with it are studied. To do so, adhesives that cure using UV light and eutectic bonding are used, where metal layers are bonded together at low temperatures.Year: 2013Funding: DFG - Transregio 123Duration: 01/2013 - 12/2017
![]()
![]()
-
TRR 123 PlanOS – B01 Offset and inkjet printing of multimode waveguidesHow can optical waveguides be printed? Professors and young researchers from Freiburg and Hanover are trying to answer this question. The sub-project B01 has the task of producing multimodal waveguides for high light output with a width of ten to several hundred microns. The advantages of two printing procedures are used to do so: flexographic printing with high throughput and low cost, and inkjet printing with a large variability and high resolution.Year: 2013Funding: DFG - Transregio 123Duration: 01/2013 - 12/2017
![]()
![]()
-
SFB 653 - L2: Opto electronic integration of HF communication system for gentelligent componentsThe aim of the sub-project is to integrate the entire communication electronics (high frequency module, microcontroller and memory) in the interior of a workpiece.Year: 2011Funding: DFGDuration: 07/2005 - 06/2017
![]()
![]()
-
SFB 653 – K1: Dispensed fibers for component-inherent energy transmission and optical signal couplingThe research focus is on the development of a flexible assembly and connection technology for the integration of electronic and optical components in metallic components.Year: 2011Funding: DFGDuration: 07/2005 - 06/2017
![]()
![]()
-
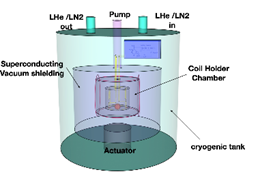
Setup of an active drop towerAs part of the establishment of the Hannover Institute of Technology (HITec), an active drop tower, the Einstein-Elevator is being set up by the Institute of Transport and Automation Technology (ITA). The design, development and construction of the facility are being carried out in collaboration with the QUEST Leibniz Research School (QUEST-LFS) and the Institute of Quantum Optics (IQ). The aim is to be able to carry out experiments under conditions of microgravity, but also under different partial gravity conditions such as those on the Moon or Mars.Led by: Dipl.-Ing. Christoph LotzYear: 2011Funding: German Research Foundation (DFG) and Lower Saxony state gouvernmentDuration: since 10/2011
![]()
![]()